System Design - Twitter
本篇文章為針對 花花醬 Youtebe 所講述的內容進行筆記,一切都還是以影片中的內容為主,會知道此頻道是因為在碩班畢業前,找工作刷題時在網路上搜尋解題講解時所發現。
最近因緣際會下發現除了 leetcode 演算法外,頻道內也開始有一些系統設計相關的內容,內容都講得非常好且多半都配合圖解來模擬運行時的邏輯,有需要的大大們可以去上面挖寶 XD
Interview Signals
- Work Solution
- Analysis and communication
- Tradeoff Pros/Cons
- Knowledge Base
Overview
- Clarify the requirements
- Capacity Estimation
- System APIs
- High-level System Design
- Data Storage
- Scalability
1. Clarify the requirement (系統規模)
- Requirements
- Traffic size
- Nobody expect you to design a complete system in 30-45 mins
Discuss the functionnalities, align with interviewers on components to focus.
Type 1 : Functional Requirement
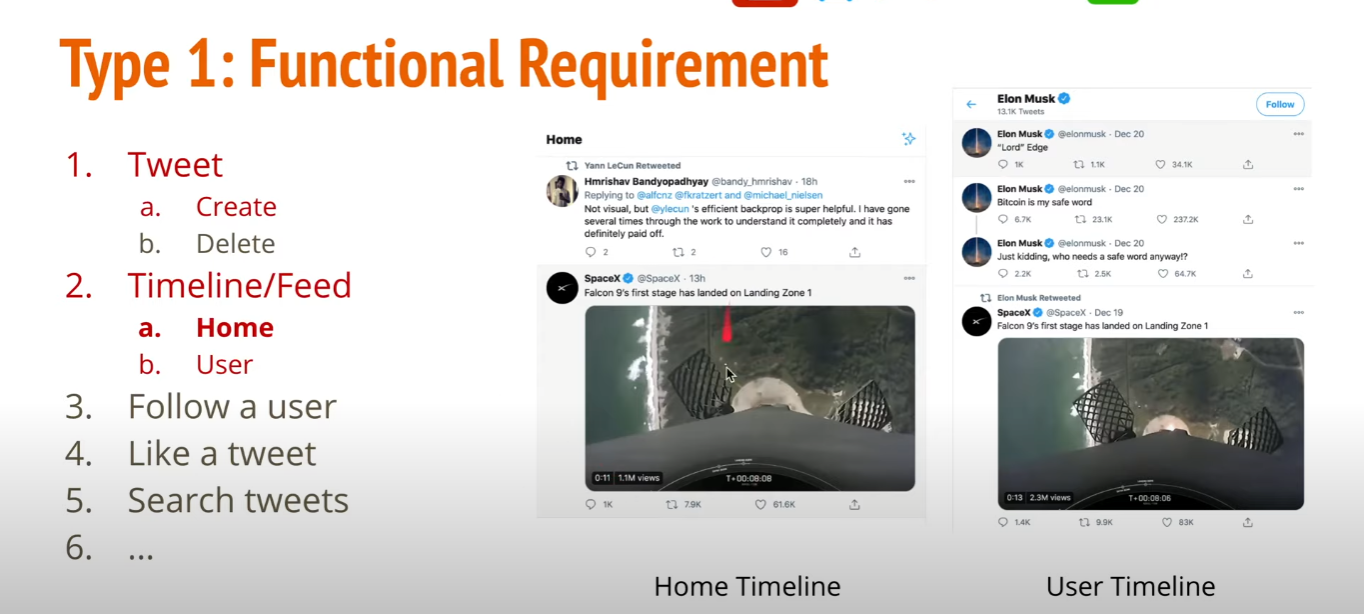
Type 2 : Non-Functional Requirement

2. Capacity Estimation (規模估算)

Storage Estimate
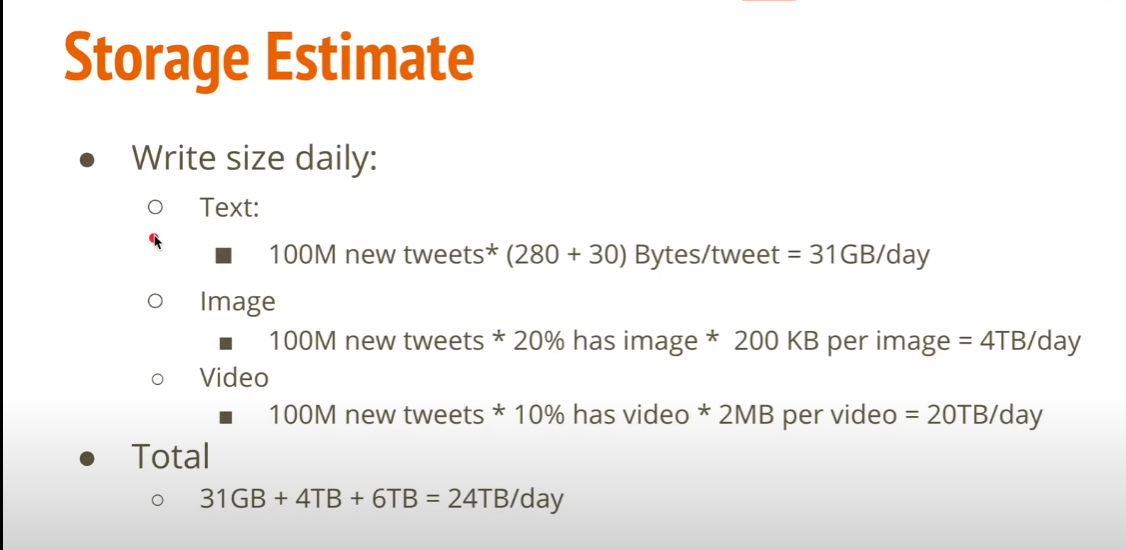
Bandwidth Estimate

藉由 Bandwidth 分析可以找出 bottleneck, 進而改善 scalability
3. System APIs

- pageSize 用於判斷手機或是電腦螢幕大小,藉以返回對應需要的 tweets 數量,藉以節省 bandwidth, 或者優化用戶體驗。
- pageToken 用來實現翻頁的功能
4. High-level System Design
User TimeLine
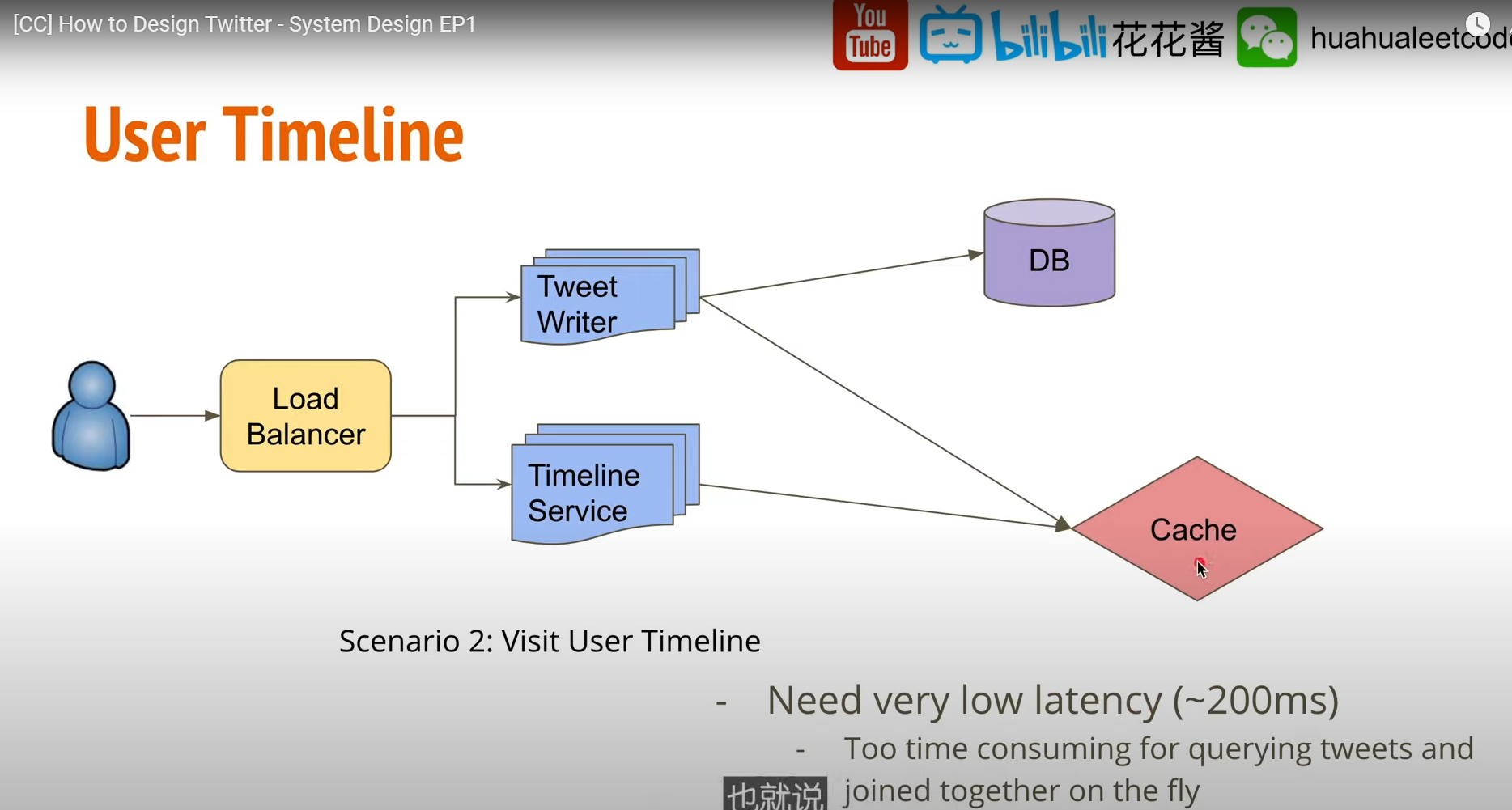
User create tweets 時 應該考慮把追蹤人數多的用戶(Elon musk)的 tweets 寫入 Cache
Home Timeline
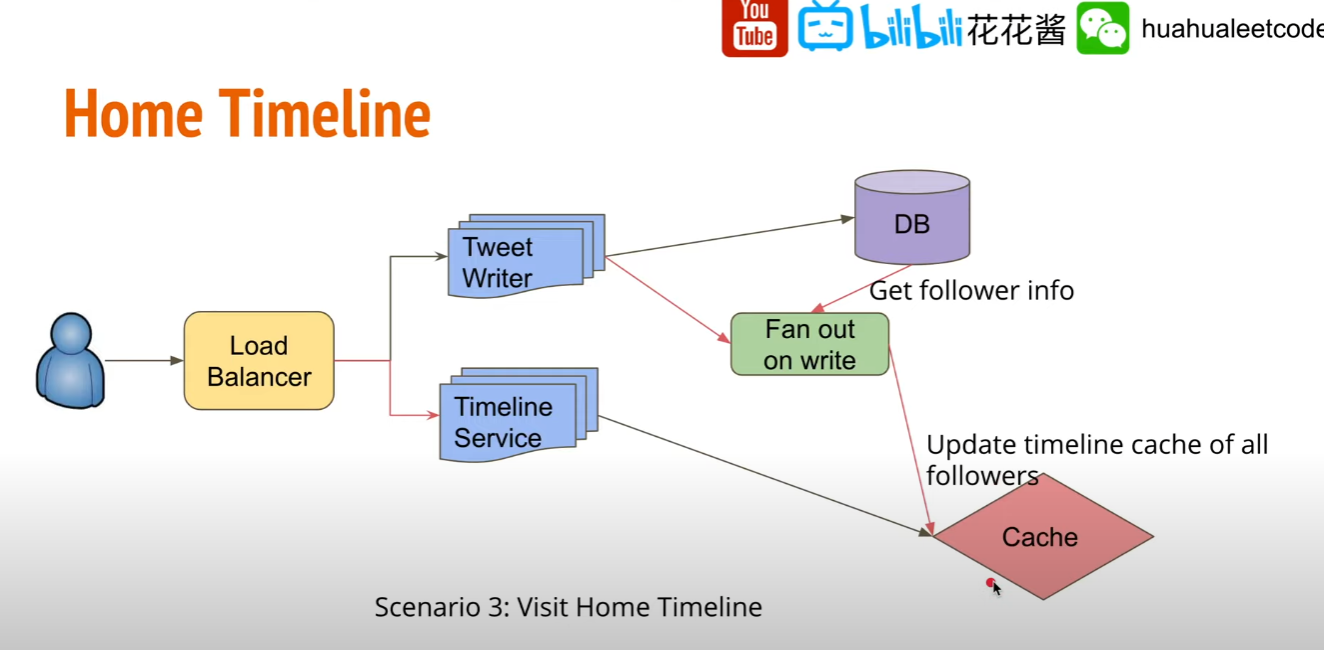
避免 TimeLine 需要每次計算,可在 cache 中預先存好每次要展示給用戶看的 Timeline
何時應該更新用戶看到的 Home Timeline?
用戶發布 Tweet 時候來更新,Tweet Writer 儲存 Tweet 時一併更新 followers 在 cache 中的 Timeline Cache.
Home Timeline (Naive) (Pull)

Home Timeline (fan out on write) (Push)
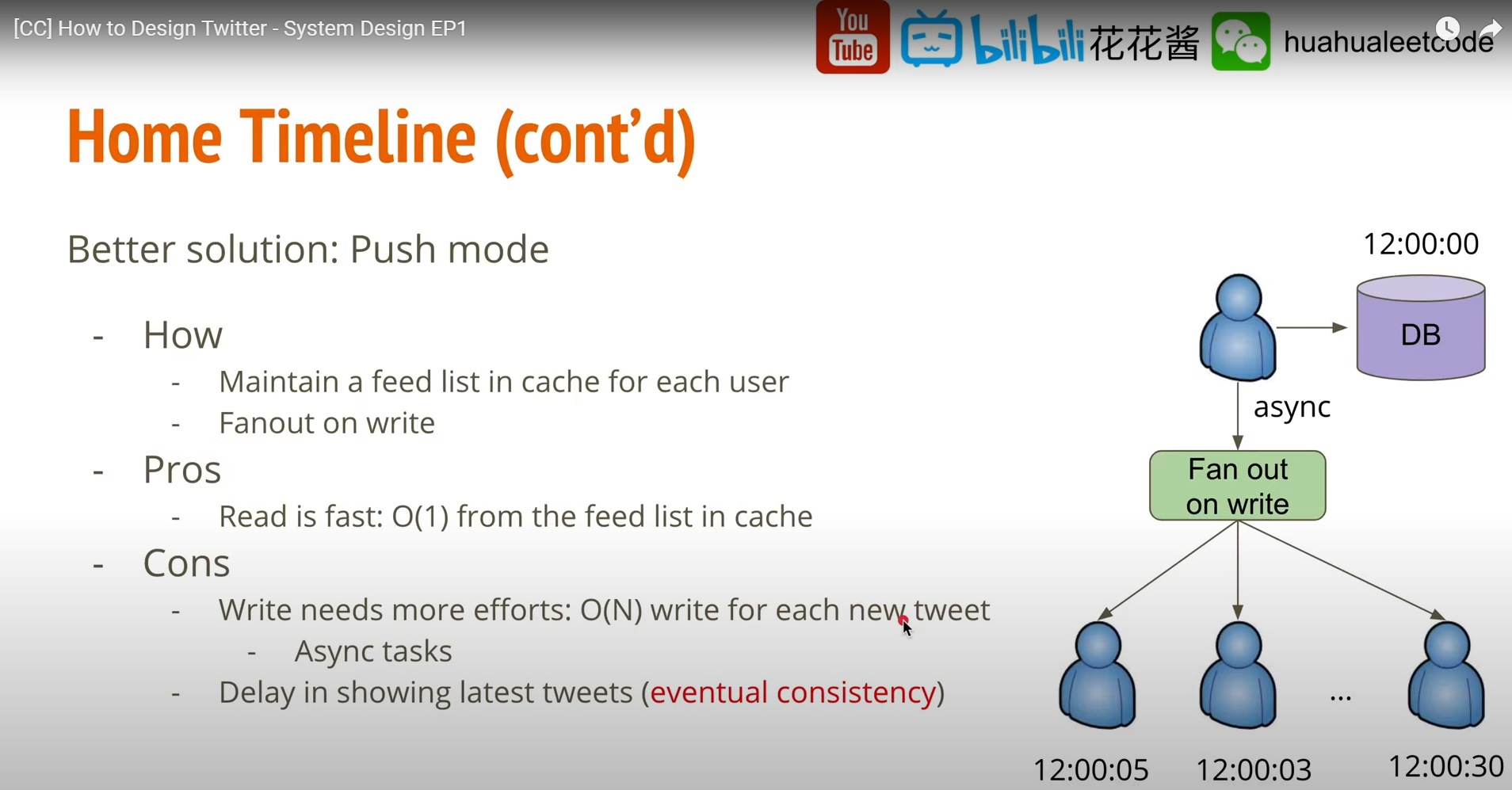
由於 write latency 對用戶而言比較不重要,可使用 async 方式慢慢做, 每個 follower 被更新的時間並不是那麼重要。
Home Timeline (fan out on write) (cont’d)

Fan out 方式有哪些侷限性?
舉例而言 Taylor swift 可能有 87.8 million followers, 若使用 fan out 的方式則會導致需要一次更新87.8 million 筆資料, 然而某些可能是 inactive user, 某些可能是假帳號, 對於粉絲數量大於 10k 的使用者使用 fan out 的方式顯然效率會不好。
使用 Hybrid 方式作為解法:
- Non-hot users
- fan out on write (push).
- do not fanout on non-active uses.
- Hot users
- fan in on read (pull): read during timeline request from tweets cache, and aggregate with results from non-hot users.
5. Data Storage
SQL Table
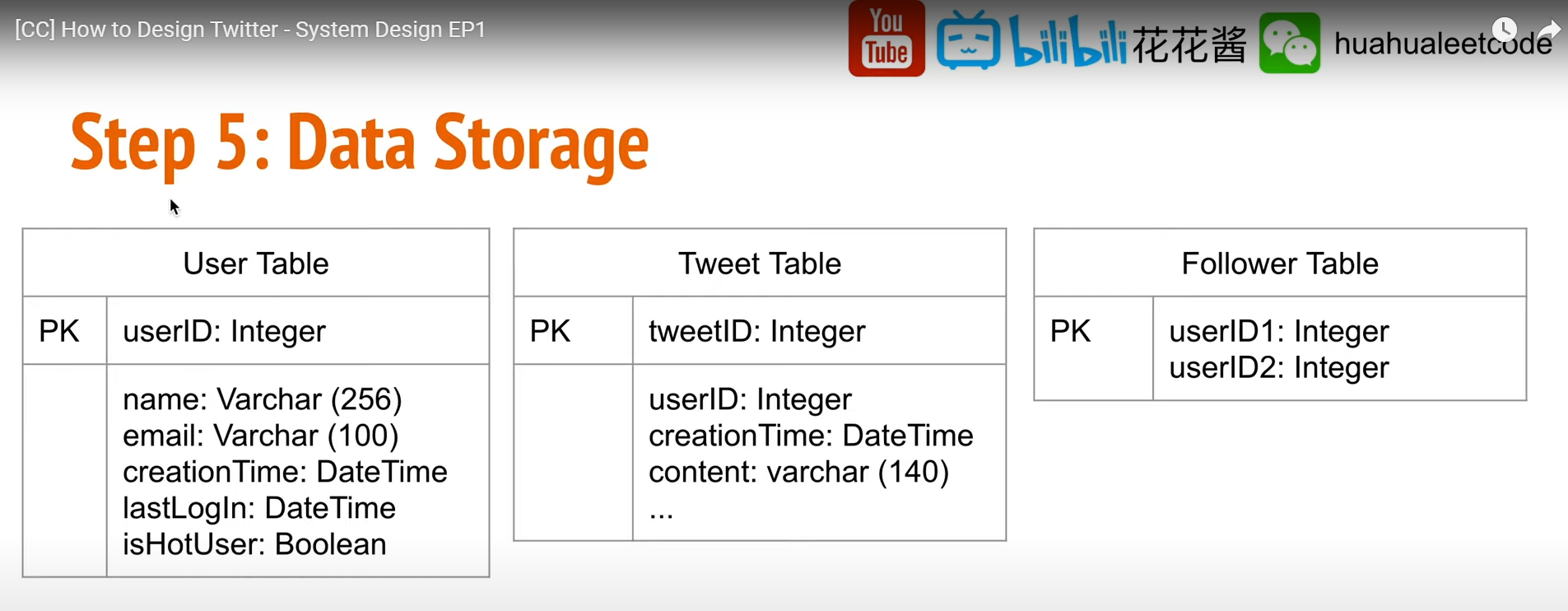
Database

6. Scalability
- 找出 bottlenecks
- 探討解法,以及每個解法的 trade-off
- Data Sharding : 如何把 data store 在不同的 server 上, 使得 read 時可以更 stable
- Load Balancing: 大量的用戶 request 如何把它 assign 到不同的 server 上, 使得每個 server 的負載達到平衡。包含 user 跟 application 之間,以及 application server 跟 cache server 之間抑或是 application server 跟 database 之間。
- Data Caching: 解決 read haevy 問題。
Data sharding
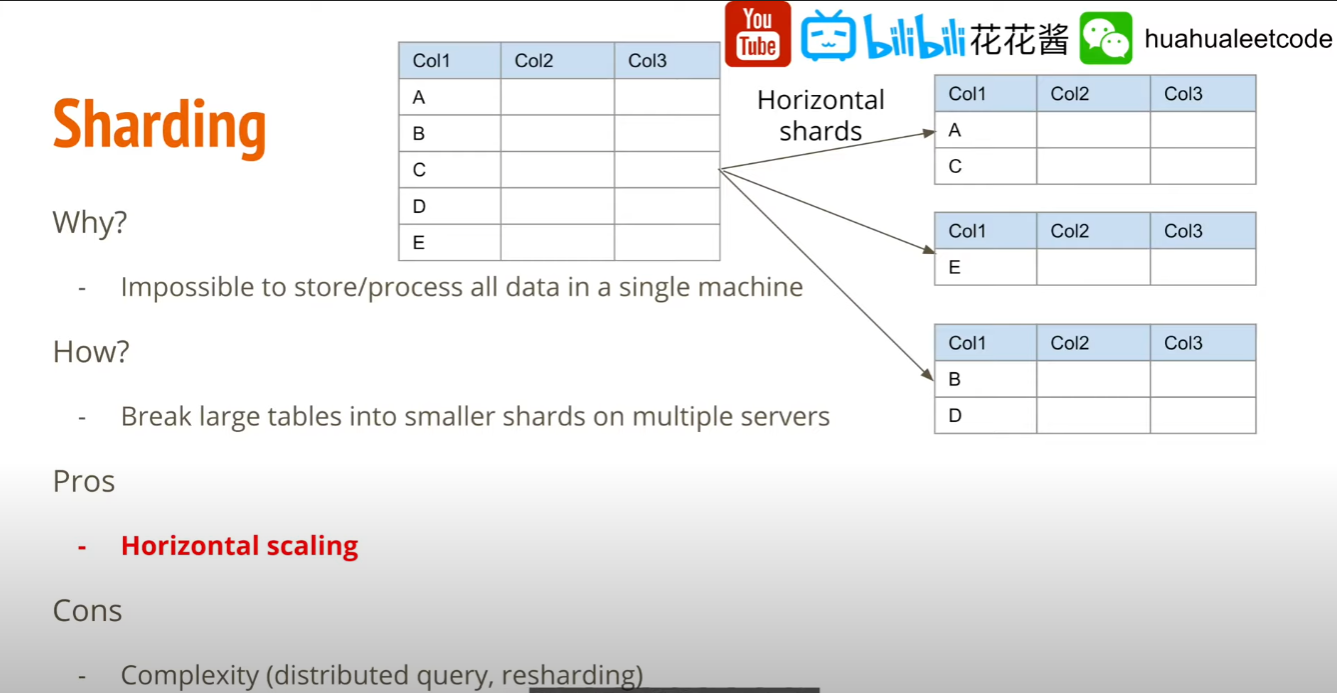
由於資料量過大,全部存在一章表是不可行的,應該將其切成一個一個的小塊(shard), 可以把一個個的 shard 存儲在不同的服務器上面,藉此解決 horizontal scaling 問題,只要機器增加的速度大於 tweet 產生的速度,則理論上可以無限地擴展下去。
Data Sharding (Shard by creation Time)

利用 timestamp 進行 shard
- Pros
- 可以簡易的用時間得到 tweet 的儲存位置, 可降低不必要的 task 數量
- Cons
- Hot/Cold data 問題,twitter 很重時效性,最近被創建的 table tweet read / write 的量會遠大於過去的 tweet 的 table, 時間久遠的 tweet 讀到的機率也會很低 (資源浪費)。
Data Sharding (Shard by hash userId)
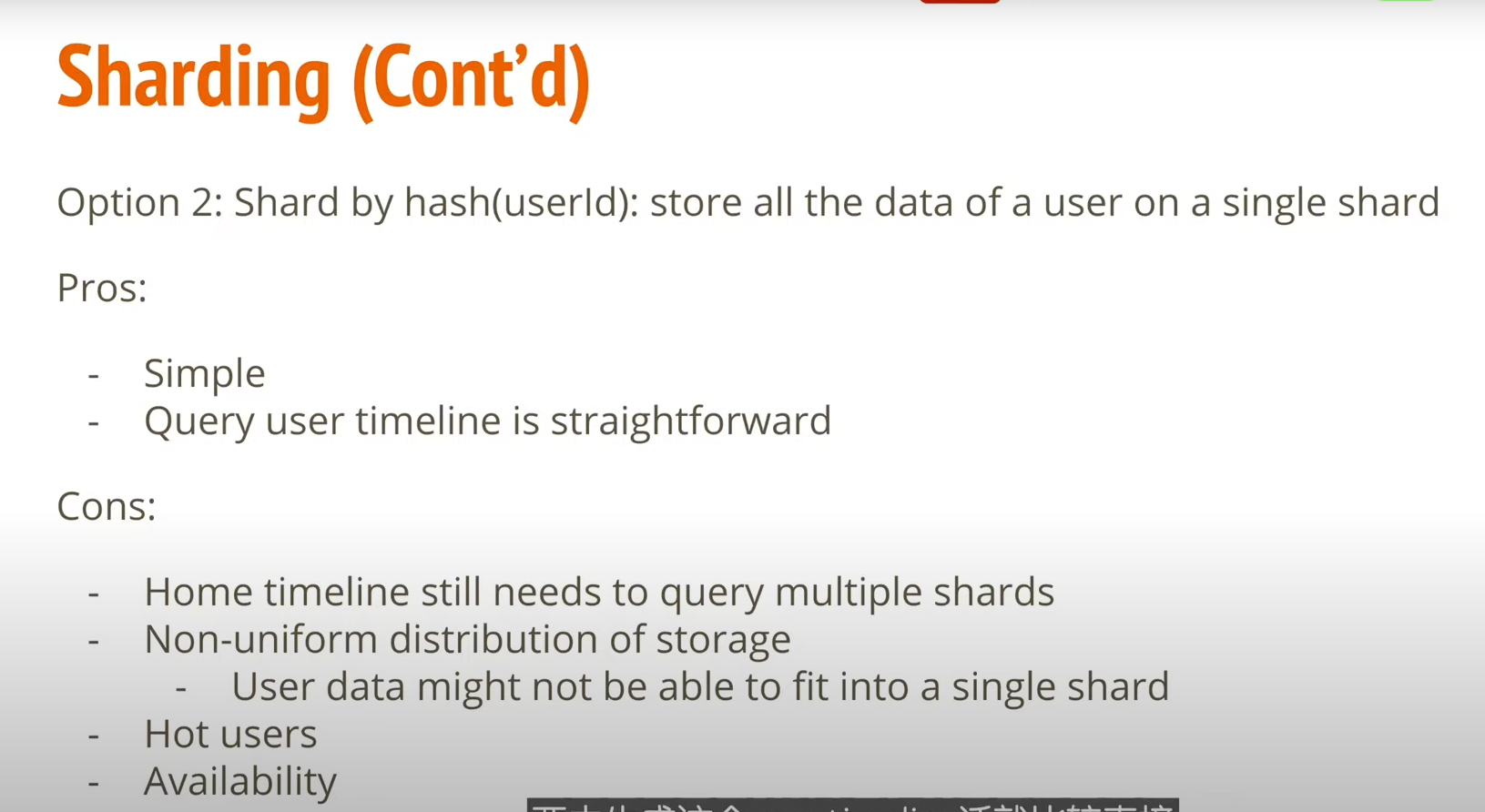
利用 userId 進行 hash 並取 mod,最後儲存到對應的 shard
- Pros
- 簡單
- 一個用戶的數據都儲存在同一個 shard。
- Cons
- Home tineline 還是要 query 很多的 shard.
- 有可能有數據太大沒有辦法放進一個 shard 的情況。
- Hot user 導致該 shard 會負載太重,會間接影響 availablity.
Data Sharding (Shard by hash tweetId)

利用 tweet id 進行 shard
- Pros
- 即便是 hot user, 還是會因為 tweetId 的緣故平均分配到不同的 shard.
- 高可用性
- Cons
- generate user/home timeline 時候一樣需要 query all shard (可以透過 cache 來解)
Caching
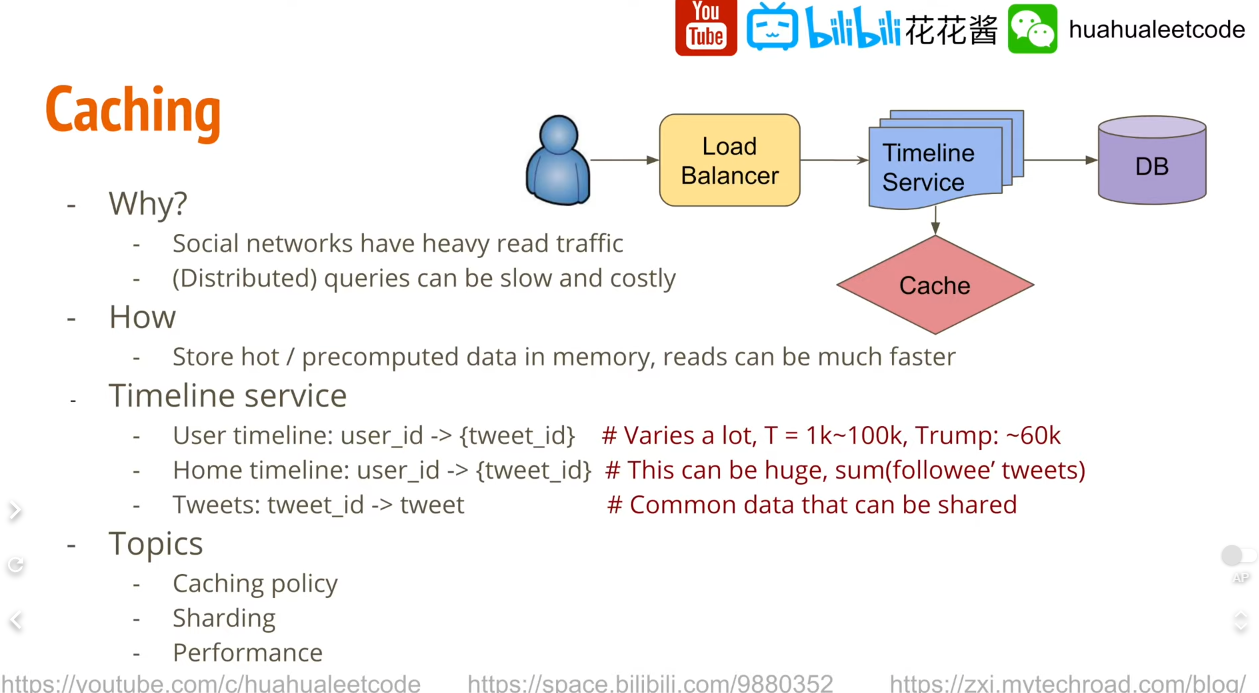
由於 social network application 的特性, heavy read traffic, 要產生像是 home timeline 這種頁面因為要大量的 query 會比較慢,因此使用 cache 來解決,將 hot query 儲存在 cache 中,避免大量的對 DB 進行 hit。
cache 中存甚麼?
- key: userId, value : tweets id list
- 只需要存最近的幾千條, 其他放 DB
- tweetId → tweet content 的 mapping table
Topic
- 應該使用 LRU, LFU 抑或是其他的 caching policy ?
- cahce 應該如何做 sharding
- capacity 以及 performance
結論
更完整的設計細節可以參考這個 Repository ,當中有許多經典面試題目:)
Reference
System Design - Twitter

